Today’s digital, hyper-connected world has enhanced our lives, both personally and professionally. The internet, mobile devices, cloud computing, social networks and a dozen of other things enable us to be connected to each other all the time. They also allow us to work remotely, and to conduct our entire business online (for example, e-commerce stores).
But this rapid technology development brought with it a rising threat: cyber-crime.
Book a demo today to see GlobalDots is action.
Optimize cloud costs, control spend, and automate for deeper insights and efficiency.

Generally, web threats are malicious software programs designed to target online users. They can appear in many forms such as viruses, spam, phishing, spyware, adware, bots and other versions of cybercrime designed to infect victims’ computers. These programs are installed without the consent of users and can cause a number of unpleasant effects, such as crippling computer performance, mining systems for personal data, erasing data or even adversely affecting the operation of computer-controlled hardware.
In this article we’ll take a look at web security basics, such as types of malicious cyber-attackers, most common cyber-attack types, and how to protect yourself from them.
Types of malicious cyber-attackers
As more sophisticated ways to infiltrate user systems are being developed, the malware market is constantly expanding. Cybercriminals use malware to harass their targets or to steal sensitive data.
Those who execute those kinds of attacks are usually:
Extortionist – Threaten to disable a website and then demand ransom money to prevent an attack.
Exfiltrators – Use decoy attacks to divert attention from their real objective – stealing data they can monetize, whether that’s intellectual property or credit card credentials.
Hacktivists – Different than other types of attackers, they want to make a political statement or shine a spotlight on a cause. Their attacks can seem random and are often incited by a particular news story. When they run into security controls they’re unlikely to back off.
Competitors – May disable your site to gain an advantage; or they might screen scrape information on your site, for example, to determine and beat your pricing.
Most common types of attacks
With the advent of cloud computing, organizations are rapidly moving toward cloud-based applications for many of their business processes thus eliminating the need for costly appliances consisting of on-premise hardware and software solutions. Cloud delivery eliminates many of the security issues that plague traditional business-technology systems such as patching and software misconfiguration.
The automation of software updates eliminates a substantial burden for the IT staff, and reduces the amount of time and expense required to manage ongoing operations.
- A rise in application layer attacks as hackers probe and exploit vulnerabilities in web service security using techniques such as HTTP floods, buffer overflow exploits, or SQL injections
- The advent of multi-dimensional attacks that combine multiple tactics and attack avenues, such as an attention-diverting DoS attack coupled with a SQL injection attack aimed at stealing data
- Dramatic growth in the scale of attacks, as attackers employ large networks of automated “bots”
- The emergence of politically-motivated “hacktivists” who seek to advance their cause with high-profile attacks on corporate or government web properties
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks
The distributed denial-of-service attack (DDoS) has as its final goal to stop the functioning of the targeted site so that no one can access it. The services of the targeted host connected to the internet are then stopped temporarily, or even indefinitely, which can cause a significant loss of revenue.
The hack is done through the master computer system that communicates with, sometimes as many as hundreds of thousands, controlled end user machines. These machines, known as zombies or bots, follow the instruction from the master system and massively launch packets at the targeted site to overwhelm the targeted machine and stop it from functioning.
Common types of DDoS attacks include:
- DNS flood
- UDP amplification
- HTTP flood
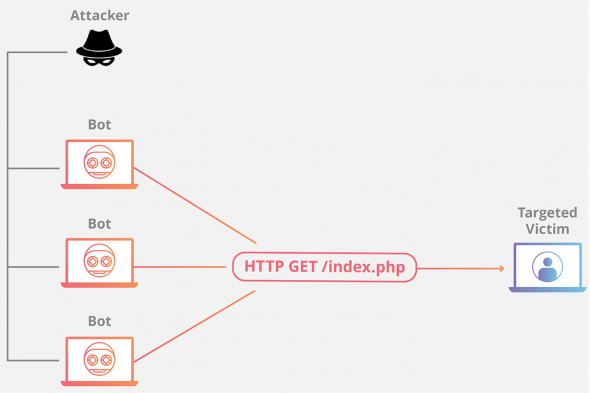
DDoS attack tools available on the internet are rapidly growing in numbers and types, but so are the techniques that try to lessen the intensity of the attacks i.e. lower the number of the packets launched at the targeted host. Those techniques are known as the DDoS mitigation methods. Packets that flood the targeted system come from multiple sources, and sometimes multiple techniques must be combined.
The attack prevention also depends on the entire internet community and their keeping of machines up to date with patches and security tools.
If you want to learn more about DDoS attacks and how to prevent them, check out our comprehensive DDoS guide.
Phishing
Phishing is a type of social engineering attack often used to steal user data, including login credentials and credit card numbers. It occurs when an attacker, masquerading as a trusted entity, dupes a victim into opening an email, instant message, or text message. The recipient is then tricked into clicking a malicious link, which can lead to the installation of malware, the freezing of the system as part of a ransomware attack or the revealing of sensitive information.
An attack can have devastating results. For individuals, this includes unauthorized purchases, the stealing of funds, or identify theft.
Moreover, phishing is often used to gain a foothold in corporate or governmental networks as a part of a larger attack, such as an advanced persistent threat (APT) event. In this latter scenario, employees are compromised in order to bypass security perimeters, distribute malware inside a closed environment, or gain privileged access to secured data.
Bad Bot threats
A bot is a software application that runs automated tasks (scripts) over the Internet. Typically, bots perform tasks that are both simple and structurally repetitive, at a much higher rate than would be possible for a human alone. The largest use of bots is in web spidering (web crawler), in which an automated script fetches, analyzes and files information from web servers at many times the speed of a human. More than half of all web traffic is made up of bots.
Bad bots scrape data from sites without permission in order to reuse it (e.g., pricing, inventory levels) and gain a competitive edge. The truly nefarious ones undertake criminal activities, such as fraud and outright theft.
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) provides a list of the different bad bot types in its Automated Threat Handbook.
Left unaddressed, bad bots cause very real business problems that could harm the success — or even the continuance — of your organization.
If you’re interested in learning more about current Bad Bot threats, and how to prevent them, check out our free Bad Bot Report 2018.
Conclusion
This article was just a short introduction into various modern web threats. We’ll take a deeper look at various cyber-attacks techniques, and how to prevent them, in following weeks. Until then, if you have any questions about how we can help you protect your website and business from bad bots, contact us today to help you out with your performance and security needs.






