Instant purging is key to any CDN as it allows businesses to remove stale, outdated and unwanted content from the edge as quickly as possible. This feature is important to publishers as well as other parts of the web industry that updates info fast (such as social networks, news portals, trading platforms).
When talking about purging, a not a one-size-fits-all approach does not exist. Some CDNs do it in seconds or minutes (referred to in the industry as “instant”), while others can take hours or longer. CDNs that take fewer time tend to adopt an asynchoronous approach and are backed by newer hardware and optimized scripting, as opposed to those that take longer because of their outdated systems or bloated networks.
Book a demo today to see GlobalDots is action.
Optimize cloud costs, control spend, and automate for deeper insights and efficiency.

There are hundreds of instances of digital media sites releasing stories, then needing to purge them due to story updates, misinformation from sources, and editorial mistakes. Depending on the reach of the website and importance of the piece, each second a false piece remains live could equate to a high-percentage loss of reputation. Purging is directly connected to the decreasing of customer experience. Another benefit or example is that after deploying new code, developers don’t have to wait forever to see the change on the production website.

Purging is shown to be most important in industries such as: publishing, advertising, gaming and software related industries.
The difference between Purging and Invalidation
Today, files are cleared from the cache in one of the following ways:
- Purging (asynchronous)
- Invalidation
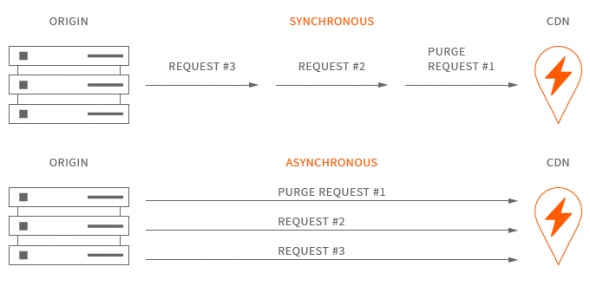
Purging today is done asynchronously, but that wasn’t always the case. While the purging requests would be submitted at the same time, they would have stand in the queue, waiting for the execution. One request had to be completed before the other one could start. The picture below shows how the requests are queued in both cases.
Purging: Secure but not always instant
Purging occurs when the CDN looks for the file on all edges and deletes it from the disk. Depending on the CDN you’re using, this can be a slower process, but it’s always more secure. The speed of the purge depends on hardware type, network size, and the amount of CDN customers requesting purges at the same time. Outdated hardware or network congestion always impacts purging to take longer time.
Some news agencies have SLAs in place that require all content be completely removed from all physical disks, due to security reasons. Invalidation can be performed instantaneously – often regardless of the CDN provider you have – and uses much less resources, mainly because the CDN only checks the header information and doesn’t require disk cycles for deletion. There is a downside though, content is still locally cached on servers and requires disk space on the edge. If the content is a large media file, that space could be used for more popular objects.
Invalidation: Faster (instant) but doesn’t meet SLAs
When invalidating content we make the Last-Modified header on the content to change. More about cache validators can be found here. This forces the validation of the origin server and based on response it will use the resource either from edge (nothing has changed) or get the latest version from the origin. In this case CDN only checks the header information and doesn’t require disk cycles for deletion. This may require extra storage capacity on the edge.
Purging methods used by different CDNs
We’ll take a quick look how different new generation CDNs handle purging methods:
- MaxCDN Instant purging. After the purge is requested, the cache is purged within seconds. In this image of the control panel, you can see that files can be purged by zone or file path.
- Akamai Purging with Queue. Akamai lets users purge content through its content control utility (CCU) that involves things like queueing and emergency queueing.
- Fastly Instant Purging. On their purging page, Fastly claims the following: “When you or your database app updates an object, the old object is automatically purged in less than two seconds from every server in our network.”
- Cloudfront Invalidation. According to this Cloudfront document, you can only invalidate objects or use object versioning to serve a different version of the object.
- EdgeCast Instant Purging. Referred to as Pirahna Purge, Edgecast states it can purge the cache 40 to 80 percent faster than competitors.
Server speed and resources we have today, made fast content removal from a CDN possible. Disk usage is still a factor, but the purging experience has greatly improved and will without a doubt continue to grow and be optimized.
In any case, instant purging is one of the critical features of modern CDNs, improving on the speed in which the stale information is cleared from edge servers and increasing the validity of information provided on CDNs customers websites. Depending on the use case customers can decide on the strategies and implementation tactics .






