Modern applications are built for speed, not simplicity. Containers, microservices, and cloud-native deployments have blown up the security perimeter. Traditional tools can’t keep up with this complexity.
That’s why Web Application Firewalls (WAFs) matter. But the WAF of 2025 isn’t just an appliance sitting in front of a static website. It’s a flexible, cloud-aware security control that adapts to the way apps are built and deployed now.
Book a demo today to see GlobalDots is action.
Optimize cloud costs, control spend, and automate for deeper insights and efficiency.

In this article, we’ll break down what modern WAFs are, how they work, where they struggle, and why they remain a foundational layer in any serious cloud security stack.
What Is a Web Application Firewall (WAF)?
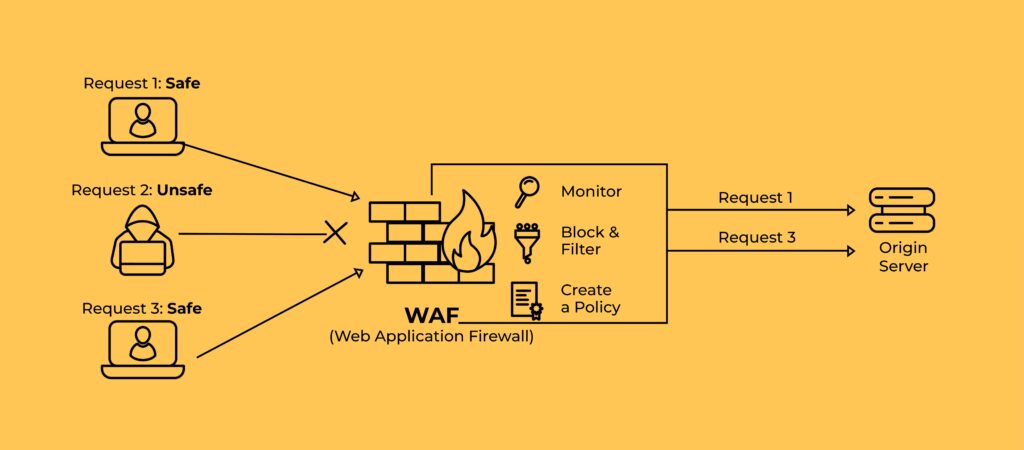
A Web Application Firewall (WAF) filters, monitors, and blocks HTTP and HTTPS traffic between a client and a web application. It sits between the internet and your app, acting as a reverse proxy that enforces security policies at the application layer.
WAFs are built to detect and block application-layer attacks — the kind that exploit user inputs, application logic, or poor access controls. These attacks often slip past traditional network defenses because they look like normal web traffic on the surface.
WAFs inspect every request with context. That includes headers, cookies, request paths, and payloads. Modern WAFs can also factor in user session data and known behavioral patterns.
Core Threats WAFs Help Mitigate
WAFs are a primary control for defending against:
- SQL injection
- Cross-site scripting (XSS)
- Broken access controls
- Cross-site request forgery (CSRF)
- Security misconfigurations
- DDoS attacks (via rate limiting)
- Server-Side Request Forgery (SSRF)
- API abuse and bot traffic
- Bot management (via device fingerprinting, browser behavior analysis, CAPTCHA enforcement, etc.)
They’re also considered a first line of defense against the OWASP Top 10, making them essential for application-layer risk management and compliance.
What Makes a Modern WAF Different?
Legacy WAFs often rely on static, signature-based rules that require frequent manual tuning. They struggle with API-driven traffic and can’t scale with cloud-native architectures.
Modern WAFs solve this with:
- Cloud-native deployment models
- Machine learning for anomaly detection
- Real-time threat intelligence feeds
- Automation for policy updates and attack mitigation
The best WAFs do more than just block known attacks. They learn from your traffic, adapt to new patterns, and integrate cleanly into DevOps workflows.
Cloud WAFs vs. Traditional WAFs
The shift to cloud-native development broke the old perimeter. Traditional WAFs, which are often deployed as hardware appliances or VM-based middleboxes in data centers, were designed for monolithic web apps behind static front doors.
That model no longer fits.
What Makes a Cloud WAF Different?
Cloud WAFs are built for elasticity, scale, and modern deployment needs. They sit closer to the application edge, integrating directly with CDNs, API gateways, and cloud-native infrastructure.
Here’s how they differ:
| Feature | Traditional WAF | Cloud WAF |
| Deployment | Hardware or virtual appliance in data center | Delivered as a managed SaaS or cloud-native component |
| Scalability | Manual provisioning and reconfiguration required | Automatically scales with traffic and app footprint |
| Updates | Manual policy and rule updates | Real-time threat feeds and auto-patching |
| Maintenance | On-prem security team responsible | Vendor-managed; minimal ops overhead |
| Fit for APIs and microservices | Poor | Strong – integrates into distributed, containerized environments |
Why the Cloud Model Wins for Most Teams
- Faster time to protection: Cloud WAFs can be deployed in minutes, not weeks.
- Integrated threat intelligence: Vendors often aggregate threat data across customers.
- More coverage for modern architectures: Critical for protecting Kubernetes, serverless functions, and globally distributed applications.
While traditional WAFs still serve niche use cases, such as air-gapped deployments or legacy compliance constraints, most organizations are moving toward cloud-delivered or hybrid WAF models for flexibility and scalability.
WAFs vs. NGFWs: Do You Need Both?
The lines between WAFs, next-generation firewalls (NGFWs), and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) often get blurred. But each tool solves a distinct problem, and lumping them together can leave gaps in your security posture.
Core Focus Areas
| Security Tool | Layer | Primary Focus | Proxy Type | Best At |
| WAF | Layer 7 (Application) | Inspects and filters HTTP/S traffic to and from web apps | Reverse proxy | Blocking OWASP Top 10, API abuse, XSS, SQLi |
| NGFW | Layers 3–7 | Enforces user and app-level access controls for outbound/inbound traffic | Forward proxy | Network segmentation, malware detection, user-based policies |
| IPS | Layers 3–4 (some Layer 7) | Detects known threats and anomalous patterns using signatures | Inline or passive | Blocking exploits, scanning for known CVEs, rate-based anomalies |
A WAF sits in front of the app, interpreting traffic in context: session IDs, cookies, HTTP methods, query strings. A NGFW guards network boundaries, filtering traffic based on IPs, ports, or apps. An IPS monitors traffic patterns for signs of intrusion, often before it even reaches the app.
Complementary, Not Redundant
Using a WAF instead of an NGFW is like locking your front door but leaving the windows open. The reverse is also true.
For layered security, combine:
- NGFW for network segmentation and outbound policy enforcement.
- IPS for exploit detection and real-time blocking at the network level.
- WAF for in-depth application-level protection and API defense.
Most enterprise-grade security stacks benefit from using all three, configured for distinct but coordinated roles.
Challenges of WAFs in Practice
WAFs can be powerful, but they’re not magic. Their effectiveness depends on correct deployment, tuning, and monitoring, and many teams underestimate the effort involved.
1. False Positives and Operational Overhead
Poorly tuned WAFs usually generate too many false positives. This leads to alert fatigue or, worse, unnecessary disruptions for legitimate users.
This is because of rigid rulesets, lack of context, and sometimes improper configuration or overly generic policies.
The result? Security teams either turn off key protections or spend excessive time managing exceptions.
2. Insufficient Coverage of Business Logic
WAFs excel at detecting syntax-based attacks (like injection or malformed headers). But they struggle with nuanced logic attacks where intent is malicious but syntax is valid.
For example, a user attempts to transfer funds they shouldn’t have access to, but uses a perfectly valid request. A WAF won’t catch it unless it understands the app’s authorization logic, which it doesn’t.
This is where runtime protection or behavior-based solutions often fill the gap.
3. Visibility Gaps in Complex Environments
In multi-cloud and hybrid setups, it’s easy to misroute traffic or bypass inspection altogether. If your app traffic doesn’t consistently flow through the WAF, protections won’t be applied.
Routine validation is needed to confirm 100% coverage, especially when using autoscaling groups, CDN-integrated deployments, or microservices.
4. Tuning and Maintenance Still Matter
Even cloud-managed WAFs need:
- Baseline traffic profiling
- Rule tuning (especially for custom apps)
- Logging and alert integration
- Regular policy reviews
Some modern WAFs offer machine learning-based tuning, but these still require supervision and validation.
Choosing the Right WAF
No single WAF fits every architecture or threat profile. The right solution depends on how your apps are built, where they run, and who’s managing security.
Key Evaluation Factors
- Deployment mode: Choose based on infrastructure:
- Cloud-native WAFs for dynamic workloads, API-heavy apps, and multi-region deployments.
- On-prem WAFs (virtual or hardware) for environments with strict latency, compliance, or data residency needs.
- Hybrid setups if you operate across both.
- Protection depth: Basic WAFs block common threats like SQLi or XSS. Advanced options offer:
- API security
- Bot mitigation
- DDoS rate limiting
- Behavior-based rules
- ML-powered anomaly detection
- App and API architecture compatibility: A WAF that can’t integrate into your Kubernetes clusters or API gateways won’t scale. Look for:
- Native support for containerized and serverless environments
- JSON inspection for RESTful APIs
- Compatibility with CI/CD pipelines
- Management and maintenance: Consider who will tune and monitor it:
- Fully managed services offload the burden
- Self-managed gives control but requires time and expertise
- Some tools offer auto-provisioning for fast setup
- Threat intelligence and updates: Choose a WAF that regularly pulls from threat intel feeds or integrates with your own. The best options apply new protections automatically.
- Logging and integration: Look for clean integration with your SIEM, observability stack, or cloud-native monitoring.
How GlobalDots Helps
GlobalDots supports your WAF strategy across the lifecycle:
Vendor-Agnostic Guidance
We help you evaluate and compare cloud WAFs, NGFWs, and API protection tools based on:
- Threat profile
- App architecture
- Compliance and operational needs
No vendor lock-in, just architecture-aligned advice.
Smart Deployment Planning
WAFs can’t protect what they don’t see. We:
- Map out 100% traffic coverage
- Integrate WAFs with your API gateway, CDN, or load balancer
- Align deployment with CI/CD workflows to avoid friction
Ongoing Tuning and Optimization
With managed WAF services, GlobalDots:
- Monitors traffic trends and fine-tunes policies
- Minimizes false positives without weakening defenses, and
- Provides reporting for audits and board-level oversight
A Smarter First Line of Defense
WAFs remain essential in 2025, but they’re no longer just about blocking OWASP Top 10 attacks. Today’s WAF must understand APIs, scale with your cloud workloads, and adapt to new attack patterns in real time. A legacy appliance won’t cut it.
Choosing the right WAF means aligning protection with how your applications are actually built and used. It also means ongoing tuning, not just a one-time setup. Whether you’re modernizing a stack or building cloud-native apps from scratch, the WAF strategy you choose now will shape how well you can defend against tomorrow’s threats.
Need help picking, deploying, or tuning your WAF? Talk to us. Our experts cut through the noise to deliver tailored, future-proofed application security, without vendor bias or operational drag.
Need help picking, deploying, or tuning your WAF?
Our experts cut through the noise to deliver tailored, future-proofed application security, without vendor bias or operational drag.






